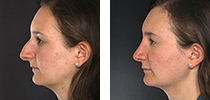
Stahl’s Ear Correction
Conveniently located to serve the areas of New York, NY
Contents
What is Stahl’s Ear?

Stahl’s Ear is characterized by an abnormal third crus, an area of cartilage in the upper ear. Although it is usually unilateral (affects one ear) it also occurs bilaterally (affects both ears) in about 20% of patients with this condition.(1)
Stahl’s Ear is informally referred to as “Spock’s Ear,” because of its resemblance to the well-known Star Trek character’s pointed ears. These features can be a source of embarrassment, leading some people to seek out surgical intervention. Studies have shown that, particularly in children, the most common motivating factor for otologic surgery was bullying, with young school-age males being affected the most.(2) But, self-consciousness about our ears can also extend well into adulthood. Although there is no evidence to show that these physical irregularities impact hearing, they can have a negative effect on confidence and body image. Luckily, there are effective surgical techniques that can help. A Stahl’s Ear correction procedure removes and reshapes cartilage of the ear for a more conventional appearance.
If you want correction of your ears, schedule a consultation with expert plastic surgeon Dr. John E. Sherman. With offices conveniently located on 5th Avenue, just across the street from the Metropolitan Museum of Art, Dr. Sherman offers experienced plastic surgery and expert patient care in Manhattan. To speak to him personally about your surgical requirements, please fill out an online inquiry form. Alternatively, you can contact our staff at (212) 535-2300 to set up a consultation.
Anatomy of the Outer Ear
Irregularities of the external ear don’t typically lead to hearing problems if no other developmental anomalies are present.(3)
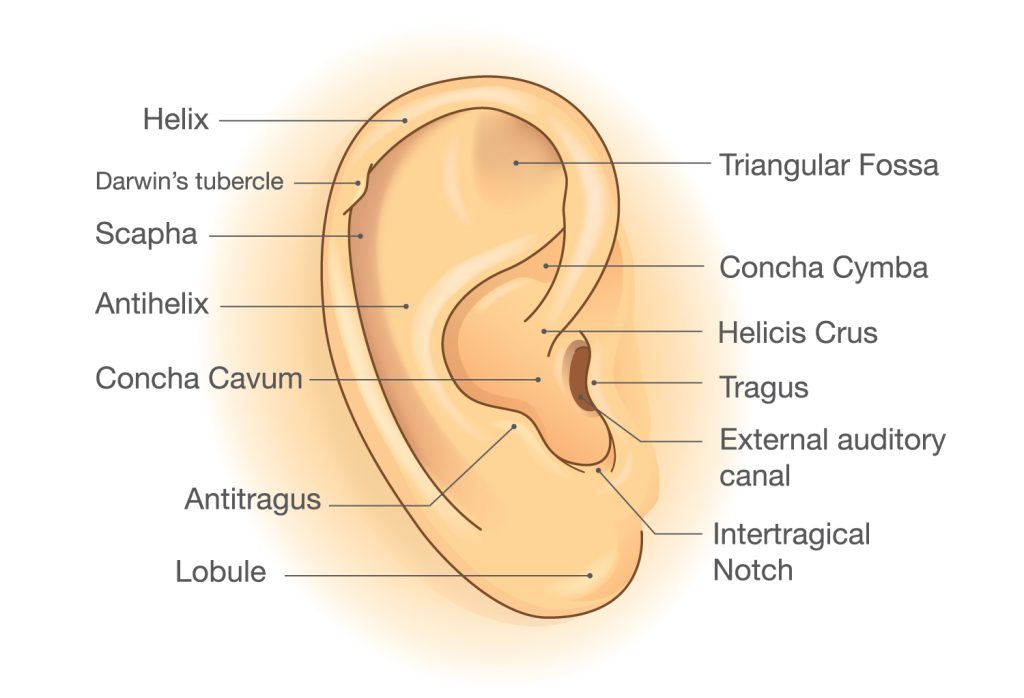
To better understand cosmetic ear correction surgery, it’s important to be familiar with some important aural anatomical features. Also known as the pinna, the auricle is the outermost protuberance of the ear and functions primarily as an amplifier to channel sound into the ear canal. It is made of flexible elastic cartilage, and is subdivided into several key structures.
(insert ear anatomy illustration)
- Helical Rim – The helix is the upper rim of the ear. In a typical ear, the helical rim curls slightly around the curvature of the auricle.
- Superior Crus – The superior crus is located toward the top of the auricle and is inferior to the helix. It is a cartilaginous ridge which combines with other auricle structures to form the shape of the ear.
- Transverse Crus – The term transverse crus, or third crus, is used to describe the defining feature of Stahl’s Ear. Rather than a normal superior crus, patients with Stahl’s Ear have a convex transverse crus that stretches diagonally upwards to the helix, creating the appearance of a pointed, elf-like tip of the upper ear.
Benefits
Stahl’s Ear is formed by an irregularity in the shape of the cartilage of the upper auricle, and as such, it can be successfully reshaped.
The procedure to correct Stahl’s Ear addresses the transverse crus, replacing the pointed shape of the upper ear with a more standard, rounded appearance. Leading New York plastic surgeon Dr. Sherman performs this precise surgery along with other otoplasties, including procedures to correct macrotia and prominent ear. One of the main reasons patients receive otological surgery to their outer ear is for cosmetic reasons, and these procedures can have a significant impact on their self-esteem. For younger patients in particular, regularly shaped ears can improve social acceptance and body image: two factors that can have a long-lasting influence on their social and academic development. Whether with young patients and their parents, or older patients seeking a long-awaited change, Dr. Sherman understands the impact this surgery can have on a patients’ life. He will discuss the considerations that accompany this procedure thoroughly during a personal consultation.
Personal Consultation
Your consultation is an opportunity for Dr. Sherman to get to know more about you, and your ears. You have an honest discussion about how your ears are currently impacting your life. After Dr. Sherman examines your ears, he will be able to assess the severity of your condition and discuss the steps necessary for a surgical correction. With his expert advice, you will then arrange a date for your Stahl’s Ear correction surgery. For your convenience, Dr. Sherman also offers virtual patient consultations.
Stahl’s Ear Correction Procedure
Stahl’s Ear is most commonly the result of a superior crus that is missing and instead replaced by a convex transverse crus that stretches upwards to the helical rim at the top of the ear. This not only leads to the pointed appearance of the helical rim, but also causes this portion of the upper ear to protrude noticeably from the head.
During a Stahl’s Ear correction procedure, the transverse crus and the concave abnormality in the posterior ear is removed. The helical rim is then advanced to close the area that was excised, thus creating a rounded, more typical rim shape. The missing superior crus may be created with a cartilage graft, or by manipulating the existing cartilage with incisions and sutures on the back of the ear. The operation may be performed under local anesthesia or sedation anesthesia.
To learn more about Stahl’s Ear correction, please visit Dr. Sherman’s YouTube channel. You’ll be able to watch him performing this delicate surgical procedure as he explains each step of the process.
Anesthesia

Approximately 75% of our otoplasties are performed under local anesthesia. The patient is given oral medications one-half hour before surgery to prevent any discomfort or anxiety. Since the procedure may take between two and three hours, the patient must be comfortable during this time. Some patients prefer sedation anesthesia, which is performed by a board-certified anesthesiologist in our offices. The obvious advantage is that after the intravenous sedation is started, the patient is lulled into a semi-conscious twilight state for the duration of the procedure, and wakes up once the surgery is complete.
Recovery & Results
As with any plastic surgery procedure, the body needs adequate time and good aftercare to heal. A safe and successful recovery is always Dr. Sherman’s priority. You’ll receive detailed instructions and helpful information about aftercare and managing discomfort.
After your Stahl’s Ear Correction
- Wear a dressing over the treated area for protection.
- Sleep on your back or on the opposite side of the treated area.
- Avoid intense physical activity.
- Wear sunscreen if you are spending a lot of time outdoors.
- Dr. Sherman will see you at timely intervals for suture removal, and to monitor your healing and final result.
After your Stahl’s Ear correction, you can expect some swelling that will steadily diminish over the first few weeks. For some patients, there may be discomfort, tightness, and stinging in the area of treatment but this can be mitigated with over-the-counter pain medications as needed. During this time it is vital to keep the area clean and avoid any hair or skin products that could impede the healing process.
Most patients are fully healed and enjoy their final results in 3 to 4 months after surgery. This short recovery solves an embarrassing cosmetic problem that many patients have endured for years. Don’t delay; start your journey with us today to feel better about your appearance and have the confidence you deserve.
For more information about the surgical procedures offered by Dr. Sherman, please be sure to check out his blog.
How Much Does Stahl’s Ear Correction Cost in Manhattan?
The cost of your Stahl’s Ear correction will depend on your individual circumstances, including the severity of your condition and whether Dr. Sherman is helping to correct both ears. Financing may be available to qualified candidates.
How can I fix “Spock” ears?
So-called “Spock” ears, or “elf ears” can be fixed with an effective plastic surgery technique that alters the shape of the ear, for a more standard aesthetic. Officially, the term for “Spock” ears is Stahl’s Ear. Once your diagnosis has been confirmed, your board-certified plastic surgeon can skillfully excise excess cartilaginous tissue and reform the ear to a more aesthetically pleasing shape.
Can I get plastic surgery to correct my ears?
tological surgery is frequently performed on patients who want to change the shape of their ears, most notably in malformation cases such as prominent ears (that protrude further than 2cm outward), cryptotia (where the ear cartilage is partially buried under the skin of the side of the head), and Stahl’s Ear (where an abnormal third crus may be present).
How long is the procedure to fix Stahl’s Ear?
Between two to three hours to complete.
References
- Kazi, A. A., Hirsch, S. D., & Petersson, R. S. (2020). Surgical correction of Stahl ear using cartilage-cutting and -sparing techniques. Otolaryngology Case Reports, 16, 100179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xocr.2020.100179
- Jones, E. S., Gibson, J. A. G., Dobbs, T. D., & Whitaker, I. S. (2020). The psychological, social and educational impact of prominent ears: A systematic review. Journal of Plastic, Reconstructive & Aesthetic Surgery, 73(12), 2111–2120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjps.2020.05.075
- Braun, T., Hempel, J. M., & Berghaus, A. (2014). Developmental Disorders of the Ear in Children and Adolescents. Deutsches Aerzteblatt Online. https://doi.org/10.3238/arztebl.2014.0092